In today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape, open banking is transforming the way we interact with our financial data. This comprehensive guide provides a clear and concise overview of open banking, exploring its core principles, benefits, and potential impact on consumers and businesses. We’ll delve into the mechanics of open banking APIs, data sharing frameworks, and the security measures in place to protect sensitive financial information. Whether you’re a seasoned financial professional, a tech enthusiast, or simply curious about the future of finance, understanding open banking is essential. This guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate this exciting new era of financial innovation.
Open banking, powered by secure APIs, empowers consumers and businesses to share their financial data with authorized third-party providers. This seamless data sharing facilitates the development of innovative financial products and services, leading to increased competition and greater consumer choice. From personalized financial management tools to streamlined lending processes, open banking is revolutionizing the financial industry. This guide will examine the regulatory landscape surrounding open banking, including data privacy regulations and consumer protection measures. We’ll also discuss the potential challenges and opportunities presented by this transformative technology, providing a balanced and informative perspective on the future of open banking.
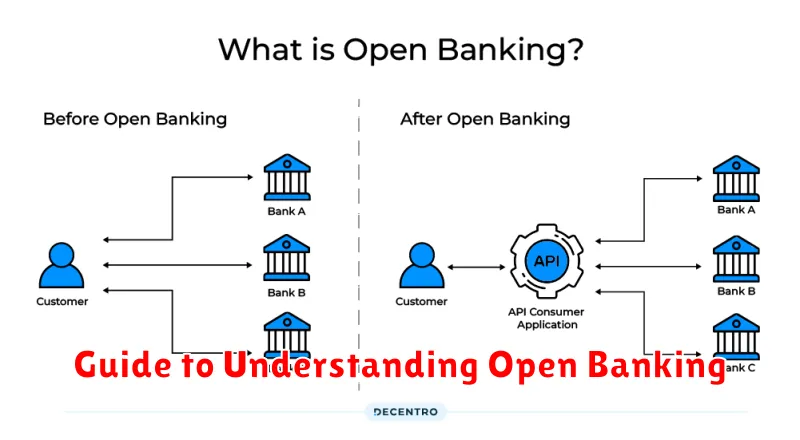
What Is Open Banking?
Open banking is a secure way to give authorized third-party providers access to your financial data. This data typically includes transaction history, account balances, and other financial information. It functions through the use of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) which allow different applications to communicate with each other.
Consent is a key principle of open banking. You choose which providers can access your data and for what purpose. This empowers you to manage your finances more effectively, compare financial products, and access innovative services tailored to your needs.
Benefits for Consumers
Open banking offers numerous advantages for consumers. Increased competition among financial providers leads to more innovative products and services tailored to individual needs.
Personalized financial management tools are another key benefit. By aggregating data from multiple accounts, consumers gain a holistic view of their finances, enabling better budgeting and spending decisions. This also empowers consumers with greater control over their financial data.
Streamlined processes, such as loan applications and account switching, offer greater convenience and efficiency. Enhanced security measures, powered by advanced technology, help safeguard consumer data and prevent fraud.
How Open Banking Works
Open banking operates on the principle of data sharing with consumer consent. It leverages Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to enable third-party providers (TPPs) to access consumer financial data held by banks.
When a customer authorizes a TPP, the bank securely shares the requested financial information. This allows TPPs to develop innovative financial products and services like personalized budgeting apps, account aggregation platforms, and more efficient lending processes.
Security is paramount in open banking. Strong customer authentication and data encryption protocols are implemented throughout the process to ensure data privacy and protection.
Security Concerns and Solutions
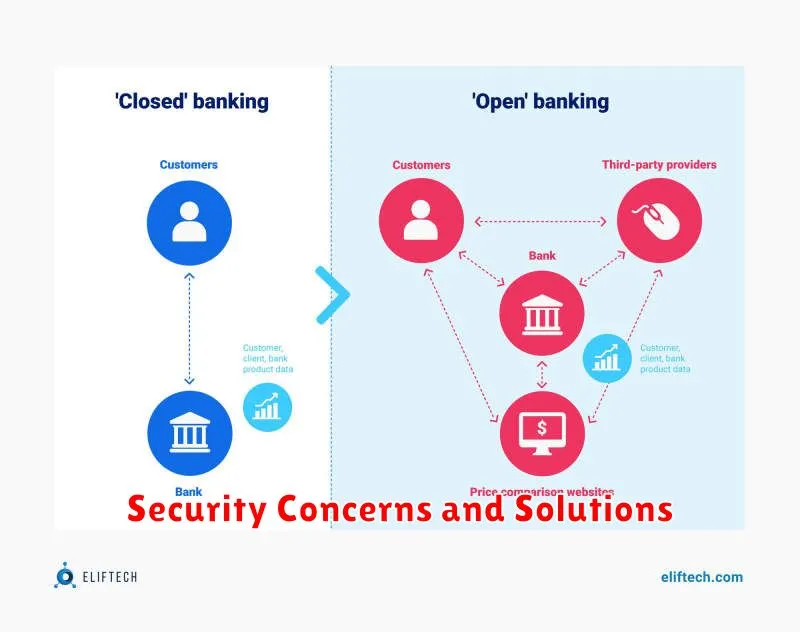
Open Banking, while offering numerous benefits, introduces potential security risks. Data breaches are a primary concern, as unauthorized access to sensitive financial information could have severe consequences. Fraud is another significant risk, where malicious actors might exploit vulnerabilities to initiate unauthorized transactions.
Addressing these concerns requires robust security measures. Strong customer authentication, including multi-factor authentication, is crucial. API security must be prioritized, employing measures like encryption and thorough testing. Data minimization, collecting only necessary data, limits the impact of potential breaches. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify and address vulnerabilities proactively.
Banks and Fintech Collaboration
Open banking fosters collaboration between traditional banks and innovative fintech companies. This synergistic relationship allows both parties to leverage their respective strengths.
Banks provide the established infrastructure, customer base, and regulatory compliance expertise. Fintechs bring technological agility, specialized services, and customer-centric design.
This collaboration can manifest in several ways, including API integrations, joint ventures, and white-label solutions. Ultimately, this cooperation expands financial product offerings, enhances customer experiences, and drives innovation within the financial services ecosystem.
Regulations and Compliance
Open Banking operates within a strict regulatory framework designed to protect consumers and ensure the security and privacy of their financial data. Key regulations vary by jurisdiction but often include data protection laws, consumer rights legislation, and industry-specific guidelines.
Compliance with these regulations is crucial for all participants in the Open Banking ecosystem. This includes obtaining necessary licenses, implementing robust security measures, and providing transparent information to customers about how their data is being used.
Regulators play a vital role in overseeing Open Banking activities, enforcing rules, and promoting competition and innovation in the financial sector. They work to maintain a balance between fostering innovation and safeguarding consumer interests.
Potential Risks to Consider
While open banking offers numerous advantages, it’s crucial to acknowledge potential risks. Data breaches are a primary concern. Should a third-party provider experience a security compromise, your financial data could be exposed.
Privacy violations are another risk. Sharing your financial data with third-party providers necessitates careful consideration of their privacy policies and data handling practices. Ensure you understand how your data will be used and protected.
Fraud and scams are a potential consequence of increased data sharing. Be vigilant about unauthorized transactions and report any suspicious activity immediately. Choosing reputable and authorized providers is crucial to mitigate this risk.
Impact on Financial Services
Open banking has significantly impacted the financial services landscape. It promotes increased competition by allowing smaller fintech companies to compete with established institutions. This competition ultimately benefits consumers with more innovative products and services, often at lower costs.
Data sharing is at the heart of open banking, empowering consumers to have greater control over their financial data. This leads to enhanced transparency and facilitates personalized financial management tools and advice.
Furthermore, open banking fosters greater financial inclusion by enabling access to financial services for underserved populations. This is achieved by leveraging alternative data sources for credit scoring and personalized product offerings.
Global Adoption Trends
Open banking is experiencing rapid growth worldwide, driven by regulatory initiatives and consumer demand for innovative financial services. Europe has been at the forefront of adoption, with the revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) acting as a catalyst.
Other regions, including Asia and Latin America, are also embracing open banking, often adapting the European model to suit their specific market conditions. North America, while progressing more gradually, is seeing increased interest from both financial institutions and fintech companies.
Key drivers for adoption include improved customer experiences, increased competition, and the development of new financial products and services. The future of open banking looks promising, with continued growth and evolution anticipated across the globe.
The Future of Open Banking
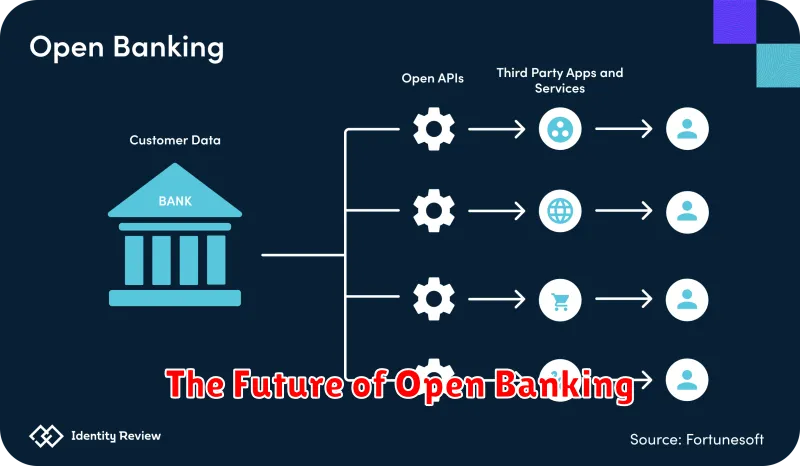
The future of open banking promises further innovation and consumer empowerment. As adoption increases, expect to see more personalized financial products and services. This includes advanced budgeting tools, tailored investment advice, and streamlined loan applications.
Standardization and interoperability will be key to unlocking the full potential of open banking. Greater collaboration between financial institutions and fintech companies will drive the development of new and improved offerings. Enhanced security measures will also be crucial to maintaining consumer trust and mitigating risks.
Open banking is poised to evolve beyond simply sharing account information. The integration of smart contracts and blockchain technology could revolutionize how financial transactions are conducted, potentially leading to faster, more secure, and transparent processes.